In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, where data generation is exploding and real-time insights are paramount, a powerful new paradigm is surging to the forefront: Edge Computing. This transformative approach shifts data processing, analysis, and storage closer to the source of data generation, rather than relying solely on distant centralized cloud data centers. The implications are profound, fundamentally reshaping how industries operate, how businesses deliver services, and how individuals interact with smart technologies. This comprehensive article delves into the core principles of edge computing, exploring its foundational technologies, diverse applications across various sectors, and the critical challenges that accompany its widespread adoption.
What is Edge Computing?
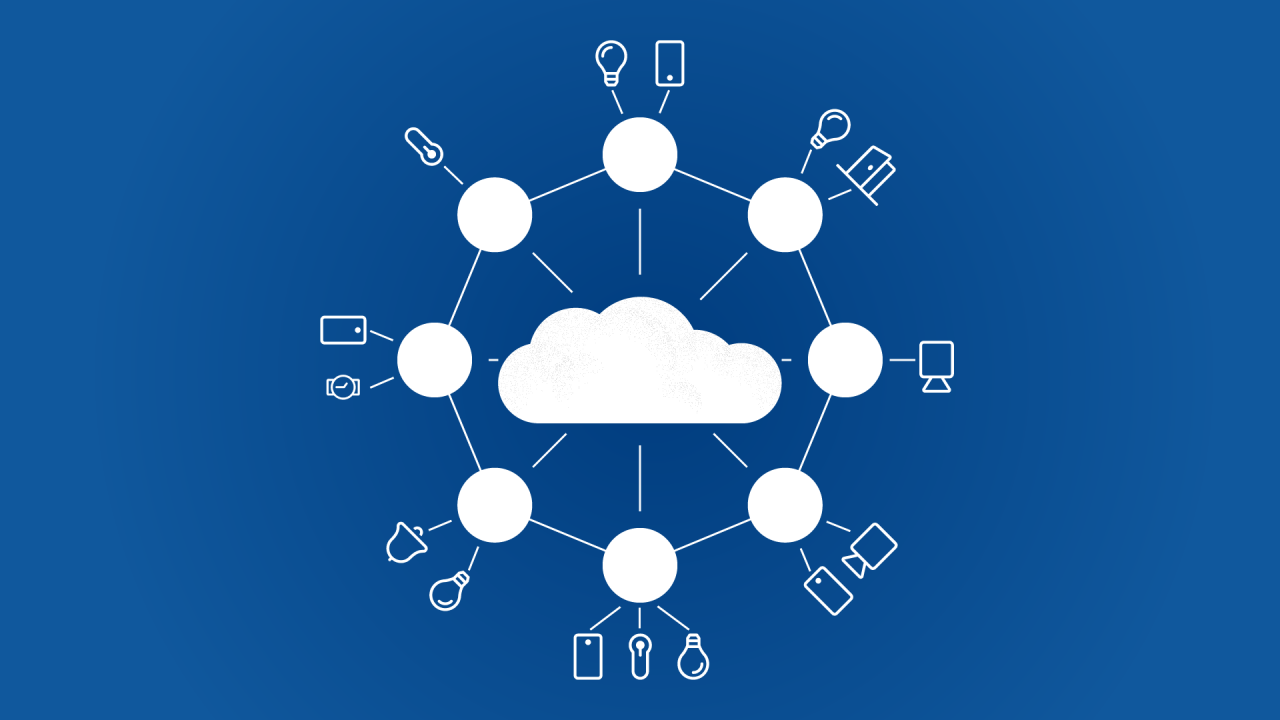
At its essence, edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the sources of data. This means instead of sending all raw data from devices (like sensors, cameras, or smart machinery) back to a central cloud server for processing, much of that processing happens right where the data is created – at the “edge” of the network. Think of it as decentralizing decision-making, allowing faster responses and more efficient use of network resources.
The need for edge computing arises from several key factors in the modern digital world:
- Explosion of IoT Devices: The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices generates massive volumes of data, often in real-time. Sending all of this data to the cloud can overwhelm networks and lead to delays.
- Need for Real-time Processing: Many applications, such as autonomous vehicles, smart manufacturing, and critical infrastructure monitoring, require instantaneous decision-making, where even milliseconds of latency can have significant consequences.
- Bandwidth Constraints: Transmitting huge amounts of raw data to the cloud can be costly and consume considerable network bandwidth, especially in remote areas or where connectivity is limited.
- Data Privacy and Security: Processing sensitive data locally at the edge can enhance privacy by minimizing the need to transmit all raw data to a centralized cloud, reducing exposure to potential breaches during transit.
Key characteristics that define edge computing include:
- Proximity: Computation occurs near the data source.
- Low Latency: Reduces the time delay between data collection and processing, enabling real-time responses.
- Reduced Bandwidth Usage: Only processed insights or critical data segments are sent to the cloud, significantly cutting down on network traffic.
- Enhanced Security: Data can be processed and secured locally, potentially reducing the risk of data in transit.
- Increased Reliability: Operations can continue even with intermittent cloud connectivity.
A. Core Components and Architecture of Edge Computing
An edge computing ecosystem involves a collaboration between various devices and infrastructure layers.
- Edge Devices (Endpoints): These are the physical devices at the very “edge” of the network that collect data. They include:
- IoT Sensors: Temperature, pressure, motion sensors.
- Smart Cameras: For video analytics in surveillance or retail.
- Industrial Machinery: Robots, manufacturing equipment.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Cars, drones.
- Mobile Phones and Wearables: Consumer devices with computing capabilities.
- Smart Home Appliances: Thermostats, smart speakers.
- Edge Gateways: These are local processing hubs that aggregate data from multiple edge devices. They often perform initial data filtering, aggregation, and pre-processing before sending relevant information to the cloud or acting locally. Gateways also manage connectivity and security for the edge devices.
- Edge Servers/Micro Data Centers: For more substantial processing at the edge, organizations deploy small-scale data centers or powerful servers closer to the data sources. These can be located in factories, retail stores, cell towers, or even within vehicles. They handle heavier computational loads, run analytics, and host applications that require low latency.
- Cloud Integration: While edge computing decentralizes processing, it doesn’t eliminate the cloud. The cloud still serves as:
- Centralized Data Repository: For long-term storage of aggregated and refined data for historical analysis, training AI models, and compliance.
- Orchestration and Management: Managing and deploying applications to edge devices and servers, overseeing the entire distributed infrastructure.
- Global AI Model Training: AI models are often trained on vast datasets in the cloud and then deployed to the edge for inference (applying the trained model to new data).
- Networking Infrastructure: Reliable, high-speed, and low-latency network connectivity is crucial, particularly 5G/6G wireless technologies, which are ideal for connecting edge devices and transporting data efficiently between the edge and the cloud.
Edge Computing’s Transformative Impact Across Industries
The shift towards processing data at the edge is fundamentally reshaping operations, creating new services, and enhancing experiences across an astonishing variety of sectors.
A. Manufacturing and Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Edge computing is revolutionizing the factory floor, enabling real-time insights and proactive management of complex machinery.
- Predictive Maintenance: Sensors on industrial equipment (e.g., turbines, robotic arms) continuously collect data on vibration, temperature, and performance. Edge devices process this data locally, immediately detecting anomalies that signal potential failure. This enables proactive maintenance, minimizing costly downtime and extending asset lifespan.
- Real-time Quality Control: High-speed cameras and sensors on production lines capture images and data. Edge AI performs immediate visual inspections for defects, ensuring consistent product quality and reducing waste without sending massive video files to the cloud.
- Automated Production Control: Edge controllers manage and optimize robotic movements, assembly lines, and machine parameters in real-time, adapting to changing conditions or material variations for optimal efficiency and precision.
- Worker Safety: Edge-enabled sensors and cameras can monitor hazardous environments, detect worker proximity to dangerous machinery, or identify abnormal movements, triggering immediate alerts or safety shutdowns to prevent accidents.
- Optimized Energy Consumption: Edge devices monitor energy usage across a factory, identifying inefficiencies and automating adjustments to lighting, heating, or machine operations to reduce power consumption.
B. Autonomous Vehicles and Transportation
Edge computing is indispensable for the functionality and safety of autonomous vehicles and intelligent transportation systems.
- Self-Driving Cars: Autonomous vehicles require instantaneous processing of sensor data (Lidar, radar, cameras) to perceive their surroundings, detect obstacles, and make split-second decisions (e.g., braking, steering) to ensure safety. This cannot rely on cloud latency.
- Traffic Management: Edge devices at intersections or along highways can analyze real-time traffic flow, pedestrian movement, and incident data locally to dynamically adjust traffic signals, reroute vehicles, and optimize urban mobility without delays from cloud communication.
- Fleet Management: Edge analytics within vehicles can monitor engine performance, driver behavior, and cargo conditions, providing immediate alerts for maintenance needs or safety issues, and optimizing delivery routes in real-time.
- Collision Avoidance Systems: Edge processing enables vehicles to rapidly analyze data from surrounding vehicles and infrastructure to predict and prevent potential collisions.
- Smart Ports and Logistics Hubs: Edge computing optimizes the movement of containers, cargo, and vehicles within large logistics facilities, reducing bottlenecks and improving operational efficiency.
C. Healthcare
Edge computing offers significant advantages in healthcare, particularly for real-time patient monitoring and data security.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Wearable medical devices collect vital signs and health metrics (e.g., ECG, glucose levels). Edge devices can perform initial analysis, detecting critical changes or anomalies locally and immediately alerting healthcare providers, without continuously streaming all raw data to the cloud.
- Smart Hospitals: Edge computing can power real-time asset tracking (equipment, beds), environmental monitoring (temperature, humidity in operating rooms), and patient flow optimization within hospital facilities, improving efficiency and resource allocation.
- Edge AI for Diagnostics: In remote clinics or ambulances, edge devices with AI can perform preliminary image analysis (e.g., X-rays, ultrasounds) or diagnose conditions even with limited or intermittent connectivity, enabling faster critical care decisions.
- Enhanced Data Privacy: By processing sensitive patient data at the edge and only sending anonymized or aggregated insights to the cloud, edge computing can significantly enhance data privacy and compliance with regulations like HIPAA.
D. Retail
Edge computing helps retailers enhance the customer experience and streamline in-store operations.
- Personalized In-Store Experiences: Edge devices analyze customer movement patterns, dwell times, and product interactions to provide real-time personalized recommendations, promotions, or navigation assistance directly on in-store screens or customer apps.
- Inventory Management: Edge sensors and cameras can monitor shelf stock levels, identify out-of-stock items, and trigger automatic reorder alerts, ensuring product availability and reducing manual inventory checks.
- Loss Prevention: Edge AI analyzes video feeds in real-time to detect suspicious activities or potential shoplifting, immediately alerting staff to prevent theft.
- Frictionless Checkout: Automated checkout systems, like Amazon Go, rely heavily on edge computing to process customer purchases, identify items taken from shelves, and manage billing in real-time without external cloud reliance.
- Optimized Store Layouts: Edge analytics can gather data on customer paths and hot spots within a store, providing insights for optimizing product placement and store layout.
E. Smart Cities and Public Safety
Edge computing is a cornerstone for the development of truly smart and responsive urban environments.
- Public Safety and Surveillance: Edge-enabled smart cameras can perform real-time video analytics to detect anomalies, identify suspicious behavior, or recognize specific events (e.g., gunshots, accidents) and immediately alert emergency services, enhancing public safety.
- Waste Management: Smart bins with fill-level sensors leverage edge processing to alert sanitation services when they need emptying, optimizing collection routes and reducing operational costs and carbon emissions.
- Environmental Monitoring: Edge sensors monitor air quality, noise pollution, and water levels in real-time, providing immediate local data for environmental protection initiatives and public health alerts.
- Smart Lighting: Edge-controlled streetlights can adjust brightness based on real-time pedestrian or vehicle traffic and ambient light conditions, optimizing energy consumption and improving safety.
- Disaster Response: Edge devices can collect and process data from affected areas during natural disasters (e.g., flood levels, structural integrity), providing immediate, localized insights for first responders, even when central networks are compromised.
Challenges and Considerations in the Edge Computing Era

Despite its surging prominence and undeniable benefits, the widespread adoption of edge computing brings forth significant challenges and critical considerations that demand careful attention and proactive solutions.
A. Security and Privacy Complexities
- Distributed Attack Surface: Edge computing inherently distributes data and processing across many devices, exponentially expanding the attack surface for cyber threats. Securing thousands or millions of disparate edge nodes is a monumental challenge.
- Vulnerable Edge Devices: Many edge devices, especially IoT sensors, are low-power and resource-constrained, making it difficult to implement robust security measures, leaving them susceptible to hacking, malware, and botnet attacks.
- Data Privacy at the Edge: While edge processing can enhance privacy by keeping sensitive data local, ensuring compliance with diverse data privacy regulations (like GDPR) across distributed edge environments adds complexity.
- Authentication and Access Control: Managing secure authentication and granular access control for a vast, distributed network of edge devices and users is a significant operational and security challenge.
- Physical Security: Edge devices can be deployed in remote or exposed locations, making them vulnerable to physical tampering or theft.
B. Management and Orchestration Complexity
- Distributed Infrastructure Management: Managing, monitoring, updating, and troubleshooting applications and infrastructure across thousands of distributed edge devices is far more complex than managing centralized cloud resources.
- Resource Constraints: Edge devices often have limited processing power, memory, and battery life, requiring optimized software and intelligent resource allocation.
- Connectivity Challenges: While edge reduces reliance on constant cloud connectivity, managing intermittent network connections, ensuring data synchronization, and handling offline capabilities at the edge remain complex.
- Software Deployment and Updates: Deploying software updates and patches to a vast array of distributed edge devices efficiently and securely is a significant logistical and technical challenge.
- Interoperability and Standardization: A lack of universal standards and proprietary technologies across different edge hardware and software vendors creates interoperability challenges and potential vendor lock-in.
C. Technical and Performance Limitations
- Hardware Diversity: The vast array of edge device types, operating systems, and computing capabilities makes it challenging to develop universal applications and ensure consistent performance.
- AI Model Deployment and Optimization: Deploying large, complex AI models to resource-constrained edge devices requires significant optimization, model compression techniques, and specialized edge AI chips.
- Data Consistency: Ensuring data consistency and integrity across distributed edge nodes and between the edge and the cloud is a complex data management problem.
- Scalability: While edge computing aims to scale, managing massive deployments with millions of devices still presents scalability challenges in terms of orchestration, data ingestion, and insights generation.
D. Cost and Economic Viability
- Initial Investment: The upfront cost of deploying edge hardware, software, and establishing the necessary infrastructure can be substantial, particularly for large-scale implementations.
- Operational Expenses: Managing and maintaining distributed edge infrastructure can incur significant operational costs related to connectivity, power, and specialized personnel.
- ROI Justification: Clearly demonstrating and quantifying the return on investment (ROI) for edge computing projects can be challenging, requiring careful planning and measurement.
E. Ethical and Societal Implications
- Privacy Concerns: While edge computing can enhance privacy, the sheer volume of localized data collection (e.g., from smart cameras in public spaces) raises new concerns about mass surveillance and potential misuse of data.
- Bias in Edge AI: If AI models deployed at the edge are trained on biased data, they can make discriminatory decisions in real-time, with immediate physical consequences (e.g., in autonomous vehicles or smart city applications).
- Accountability: When edge devices make autonomous decisions based on AI (e.g., an industrial robot malfunctioning), establishing accountability for errors or harm can be complex given the distributed nature of the system.
- Digital Divide: The benefits of edge computing may not be evenly distributed, potentially exacerbating technological and economic disparities between regions or businesses that can afford to adopt it and those that cannot.
Conclusion
Edge computing is undeniably surging forward as a critical enabler of the next wave of digital transformation. By bringing computation and data analysis closer to the source of data generation, it is unlocking unprecedented levels of speed, efficiency, and reliability, fundamentally reshaping industries from manufacturing and transportation to healthcare and retail. Its ability to provide real-time insights and enable instantaneous decision-making is proving indispensable for mission-critical applications and is key to fully realizing the potential of IoT and AI.
However, the journey into a decentralized processing future must be navigated with careful consideration. Addressing the formidable challenges of security, management complexity, cost, and the ethical implications of pervasive, localized data processing is essential for its successful and responsible widespread adoption. By fostering collaboration among technology developers, cybersecurity experts, policymakers, and industry leaders, we can ensure that edge computing serves as a powerful force for good, driving innovation at the digital frontier and building a smarter, more responsive, and ultimately more prosperous future for all. Edge computing isn’t just surging; it’s defining the very fabric of our connected world.